One of the most common causes of an Arizona workers compensation injury is either an acute or chronic shoulder problem with the rotator cuff. Tendonitis occurs commonly in middle age, with occupations that involve repetitive overhead lifting affected the most.
The humerus (upper arm) connects to the shoulder with tendons and muscles. The rotator cuff controls the arms stabilizes the shoulder and controls the rotation of the arm out away 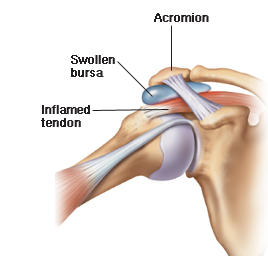 from the body, and consists of four muscle-tendon groups. Four tendons merge together to create a cap over the humerus head. This bone’s head makes up the joint known as the shoulder and gives the ability to move the arm in a full circle but the cuff could have tendinitis that limits this ability.
from the body, and consists of four muscle-tendon groups. Four tendons merge together to create a cap over the humerus head. This bone’s head makes up the joint known as the shoulder and gives the ability to move the arm in a full circle but the cuff could have tendinitis that limits this ability.
Understanding Rotator Cuff Tendonitis
Bursitis, impingement, and biceps tendinitis are all names for rotator cuff tendinitis. The cuff tendons and area around them are swollen and painful with rotator cuff tendonitis. The joint is cushioned by fluid in the soft sack known as the bursa.
Causes of Rotator Cuff Tendinitis
Rotator cuff tendinitis typically happens gradually as irritation to the area is repeated. Those who perform repetitive or heavy lifting above the shoulder, have bone anatomy that is abnormal in the shoulder or loose joints are more likely to have tendonitis in the rotator 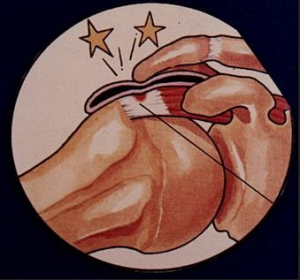 cuff.
cuff.
Pinching of rotator cuff tendons between part of the shoulder blade known as the acromion and upper portion of the arm bone (impingement) can result from either moving the arm over the head or overhead lifting. A sudden shoulder injury or calcium in the tendons can also cause it.
Stages of Injury
- Bursa becomes swollen or painful
- Limited range of motion/weakness in the shoulder resulting from a shoulder injury or irritation that has lasted for a long period of time.
- The fibers progressively weaken which can cause partial or complete tearing of the tendon during tendinitis.
Diagnosing Tendonitis
The first step of the diagnostic process is having the shoulder examined. Evaluation of the instability, weakness, pain and range of motion is done through movement and strength testing. Other bone diseases, arthritis and broken bones are ruled out as the cause of pain in the shoulder by taking x-rays.
An MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is performed is there is a tear in the cuff suspected. The MRI has the ability to detect tears that are small and partial in the rotator cuff. The diagnosis may be aided by injecting dye into the join during a process known as an arthrogram.
Treatment of Rotator Cuff Tendonitis
Resting of the injured shoulder until the swelling and pain subside is recommended. Preserving the shoulder’s full motion is done by strengthening and gentle stretching during physical therapy. It is best to avoid exercises above shoulder level since they will increase the inflammation by pinching the tendons. The shoulder may freeze or stiffness of the joint may occur if there is inactivity.
- Ice- pain and inflammation are reduced by using cold packs or ice bags. (Apply twice a day for a minimum of thirty minutes.) An ice cube can be used to massage the painful area for swelling and pain.
- NSAIDS – aspirin like drugs such as Advil or Ibuprofen can help with the pain and swelling. Your doctor can determine which one of the numerous types available is right for you. Take only as directed to help avoid potential side effects.
Steroid treatment might be used if other treatments for pain and inflammation fail to work. The drugs may be given as an injection above the tendons that have been injured. Steroid  injections are only used by Phoenix work comp doctors if specifically indicated even though they offer pain relief on a long-term basis.
injections are only used by Phoenix work comp doctors if specifically indicated even though they offer pain relief on a long-term basis.
Most of the time, injured workers will be able to obtain relief nonoperatively. The workers comp doctor in AZ can help with treatment, and most people get back to work without going under the knife.
Surgery
Surgery is not normally required for rotator cuff tendinitis without tearing in the cuff. The above treatments will typically take care of inflammation, but if the relief from treatments has been temporary after several months, the option of surgery is considered.
- Acromioplasty – A small camera is put in the shoulder joint through a small incision so the surgeon can see the area and shave the bottom of the acromion increasing the area between it and the injured cuff tendon. Irritation is prevented because of chance of pinching being decreased. Minor tears can be repaired and the damaged tissue removed.
Dr. Demitri Adarmes
Rehabilitation
Following an open rotator cuff repair or arthroscopic surgery rehabilitation typically starts the first week after the operation. Following the program recommended by the surgeon and the therapist for rehabilitation is important. It can take several months to regain strength following the surgery. A full recovery is possible.






Leave A Comment