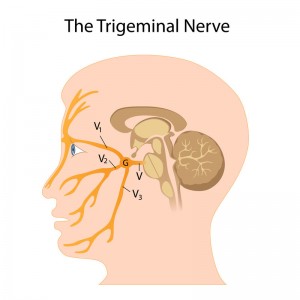
Trigeminal neuralgia, also known as Fothergill’s disease, is known for causing pain from the trigeminal nerve that runs through the face. It is considered one of the most painful disorders a person can contract and it is estimated that approximately 1 in 20,000 suffer  from this condition. It can be difficult to estimate the true number of trigeminal neuralgia patients because this condition is frequently misdiagnosed.
from this condition. It can be difficult to estimate the true number of trigeminal neuralgia patients because this condition is frequently misdiagnosed.
Symptoms of Trigeminal Neuralgia
This condition causes intense pain in the face that may last anywhere from a few minutes to a few hours. Something as slight as an air currant or light touch can be enough to trigger an episode. In some cases an episode occurs spontaneously with no trigger at all.
Attacks may affect one side of the face, but around 10 percent of patients experience symptoms across both sides. The pain is described as feeling like a crushing burning, electric shock or shooting pain across the nerve branches in the face. This pain may spread across other divisions of the nerve over time.
Best Treatments for Trigeminal Neuralgia
There are five main treatment options that are considered the most effective for managing trigeminal neuralgia discomfort.
- Gallium maltolate ointments or creams have been found to be helpful in easing
 symptoms of refractory postherapetic trigeminal neuralgia symptoms.
symptoms of refractory postherapetic trigeminal neuralgia symptoms. - Some patients have found success with using low doses of antidepressants including amitriptyline to manage their pain.
- Anticonvulsant medications that contain carbamazepine are generally used to help minimize the effects of trigeminal neuralgia. The two most commonly prescribed medications include lidocaine and clonazepam.
- In some cases duloxetine has been found to be very effective in minimizing symptoms of trigeminal neuralgia. This is particularly helpful if this condition appears to be causing depression in the patient as well.
- Opiate-based medication combined with gabapentin can be very effective in easing the neurologic pain that is often associated with trigeminal neuralgia. Oxycodone and morphine are commonly prescribed, though patients that use these medications will need to be monitored carefully as these medications can be habit forming.
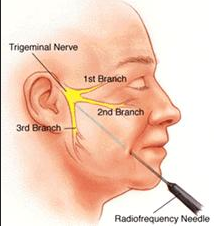 Some doctors recommend surgical therapy for trigeminal neuralgia symptoms if medical treatments have not been effective, though the success rates with surgical therapy are quite low. While performing surgery may ease the pain it can cause widespread numbness throughout the facial area that is often considered awkward or limiting.
Some doctors recommend surgical therapy for trigeminal neuralgia symptoms if medical treatments have not been effective, though the success rates with surgical therapy are quite low. While performing surgery may ease the pain it can cause widespread numbness throughout the facial area that is often considered awkward or limiting.
There are three general procedures which are used to address the symptoms of trigeminal neuralgia if all other treatment options have been exhausted. The nerve splits into three areas throughout the face, and doctors will frequently use a balloon compression to address the portion of this nerve that is causing symptoms.
This technique is more commonly used on elderly patients that developed trigeminal neuralgia along with another medical condition. Microvascular decompression is more commonly used to address the needs of patients that are experiencing pain from the ophthalmic nerve. Glycerol injections can also be used to coat the nerve to eliminate erratic pain signals but this liquid is quire corrosive to nerve fibers and can cause additional damage to the face if it is not administered properly.






Leave A Comment