by Dr. Demitri Adarmes
Although spine surgery may provide quick short-term relief of back pain due to disc herniation, studies fail to document long-term relief that is superior to the results of  conservative treatment for most chronic back pain due to disc disease or simply arthritis.
conservative treatment for most chronic back pain due to disc disease or simply arthritis.
For those who have sustained an injury with resultant chronic back pain as a result of a work injury or auto accident, low back surgery should be an absolute last resort.
Conservative management of back pain due to disc disease or arthritis exacerbations should include all of the following:
1) Medications: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) should be the first-line medication for patients with mild to moderate back pain. For moderate to severe back pain, judicious use of opioid medications is appropriate on a short term basis.
Because of its powerful anti-inflammatory effects, oral steroid medication can be beneficial in relieving back pain associated with nerve root irritation (sciatica or “pinched nerve”) or  inflammation. Low doses of anti-depressants, especially tricyclic anti-depressants, have been shown to be of proven benefit in the treatment of chronic back pain.
inflammation. Low doses of anti-depressants, especially tricyclic anti-depressants, have been shown to be of proven benefit in the treatment of chronic back pain.
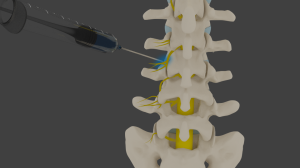
2) Epidural steroid injections: An epidural steroid injection is commonly used to treat unremitting spinal nerve root irritation (e.g., a “pinched” nerve in the neck or low back). Spinal nerve root irritation most frequently occurs either in the cervical or lumbar spine and is due to compression of the nerve root by a protruding or herniated disc.
With the aid of fluoroscopy (a specialized x-ray technique), the injection is directed to the area around the affected nerve root just outside of the tough outer membrane which encloses the spinal cord. In this way, a high dose of cortisone can be administered for maximal anti-inflammatory action around the inflamed nerve root.
3) Physical therapy: Physical therapy makes use of passive modalities such as heat, cold, ultrasound, electrical stimulation and massage when back pain is acute. A critical role of the physical therapist is to educate the patient in regard to proper posture and body mechanics in order to promote healing and prevent re-injury.
The therapist also instructs the patient in “core stabilization” exercises specifically geared toward strengthening the back and abdominal muscles so as to better support the spine. Therapeutic aquatic exercise can be very beneficial.
4) Staying active: Bed rest is appropriate for the first few days after a back injury. Then, it is time to gently mobilize the spine with low impact activities such as short walks, swimming and yoga.
5) Lifestyle changes: Obesity aggravates back pain and contributes to disc degeneration. Smoking increases the risk of developing back pain, contributes to osteoporosis and disc deterioration. Studies have shown that smoking increases pain perception and smokers require more analgesics to ease their pain.
6) Disc Injections: Injections into the disc space have been looked at for relieving the
pain from degenerative disc disease. They have been shown to typically work for a few months with simple introduction of numbing medicine and steroid. Obviously this won’t fix the problem, but it’s a low risk, outpatient option.
7) Facet Injections, Medial Branch Blocks or Radiofrequency Ablation: For those individuals having back pain from arthritis or injury to the small joints of the spine (facet joints), these injections may make a huge difference. The initial injections involve numbing medicine and possibly steroid either into the joint itself or in the immediate vicinity.
If that injection works well, it can be repeated when necessary, or a radiofrequency ablation procedure can be performed. This may provide over a year of consistent pain relief!
8) Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS): A TENS device is a small electrical unit which emits electrical impulses via electrodes attached to the skin. The electrical impulses are thought to override pain signals to the brain.
9) Chiropractic: Spinal manipulation by a licensed chiropractor or osteopath is generally considered a safe and effective treatment for acute low back pain.
10) Alternative medicine: Acupuncture, hypnotherapy and meditation are all useful adjuncts in the treatment of chronic low back pain.






Leave A Comment