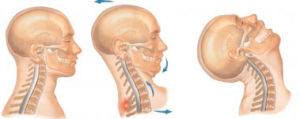
Whiplash is a laymen term used to describe injury to the soft tissues in the neck sustained when one experiences a cervical acceleration-deceleration (CAD). The term whiplash is used as it describes the rapid back and forth, whip-like, motion of the head that occurs.
While the physics of the injury is termed CAD, the term whiplash associated disorders (WAD) 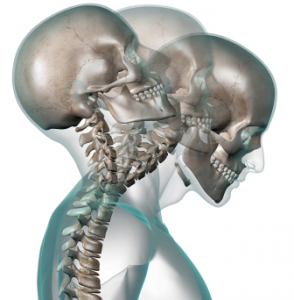 is a description of the injury sustained and the symptoms associated with the injury. The most common cause of CAD related WAP are automobile accidents where a vehicle is struck from behind (Crippling Upper Back Pain After Whiplash Aand Other Motor Vehicle Collisions Caused by Thoracic Disc Herniations: Report of 10 Cases 2014)..
is a description of the injury sustained and the symptoms associated with the injury. The most common cause of CAD related WAP are automobile accidents where a vehicle is struck from behind (Crippling Upper Back Pain After Whiplash Aand Other Motor Vehicle Collisions Caused by Thoracic Disc Herniations: Report of 10 Cases 2014)..
What symptoms are associated with whiplash?
Often the symptoms of whiplash will not occur until several days after an accident, you might wake up feeling pain and stinging sensations in your neck. The pain may then spread, radiating down through the arms and middle back, even extending into your legs. A pins and needles effect is a common complaint as well (Clinical management of cranio-vertebral instability after whiplash, when guidelines should be adapted: A case report 2014)..
How is whiplash diagnosed?
Your medical history will be taken into consideration first. If you have been in an accident that could cause whiplash further examination may warrant x-rays or other medical imaging such as an MRI or CAT scan to determine the severity of your injury ([The relationship between whiplash injury and temporomandibular joint dysfunction] 2012)..
What treatment is available for whiplash victims?
 In the past the go-to treatment for whiplash was a soft collar placed around the neck to limit mobility; modern medicine has ruled that as the WRONG thing to do. The most effective treatment for a whiplash injury is immediate, light physical therapy as strengthening exercise promotes healing and prevents further problems, (unless it’s a level 4 injury, as listed below of course).
In the past the go-to treatment for whiplash was a soft collar placed around the neck to limit mobility; modern medicine has ruled that as the WRONG thing to do. The most effective treatment for a whiplash injury is immediate, light physical therapy as strengthening exercise promotes healing and prevents further problems, (unless it’s a level 4 injury, as listed below of course).
A whiplash injury that lasts longer than six months is referred to as whiplash syndrome. Whiplash syndrome is classified on five levels, (0-4), with the lowest level meaning no pain and level 4 meaning a fractured or dislocated vertebra.
Levels 0-3 can be managed with outpatient treatments and physical therapy while level 4 requires hospitalization. Physical therapy exercises for 0-3 level injuries include light cervical rotation (turning the head side to side) until it begins to become painful, flexion and extension  (nodding the head slowly up and down as far as possible) until it becomes painful.
(nodding the head slowly up and down as far as possible) until it becomes painful.
Also, flexion/extension and rotation of the shoulder joints; these exercises are performed 3-4 times daily. Other treatments can include massage, acupuncture, non-narcotic analgesics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and botulinum toxin type-A injections for temporary pain relief (Verification of whiplash-associated disorders in forensic medical practice. part I–assessment of the injury circumstances and biomechanics 2014)..
What are the expectations when a patient gets treatment?
Depending on the level of the injury, a person suffering whiplash that undergoes some form of treatment will have different expectations. With the lower levels of injury typically a few weeks of therapy can restore normal functioning, but persons suffering level 4 injury may become permanently disabled and require ongoing treatment.
How is the procedure/treatment performed?
Physical therapy is typically done on an outpatient basis for lower level injuries; higher level injuries may require a hospital visit.
How long do the benefits of the botulinum toxin type-A injections last with this condition?
This injection provides benefit for short duration, maybe a few weeks for most patients. For higher level injury the procedure will have to be repeated.
What risk or side effects are associated with whiplash?
Most patients recover within a few weeks with proper therapy, however approximately 50% of patients will experience a long term disability due to their injuries (Effects of neck-specific  exercise with or without a behavioural approach in addition to prescribed physical activity for individuals with chronic whiplash-associated disorders: a prospective randomised study 2014).
exercise with or without a behavioural approach in addition to prescribed physical activity for individuals with chronic whiplash-associated disorders: a prospective randomised study 2014).
How successful are they the relief of pain for the condition?
As stated above, half of patients suffering a whiplash related injury usually recover within a few weeks with no long term effects. However, for the half that experience long term effects, the effectiveness of different treatments on an individual cannot be anticipated. You may find relief from one or several available treatments, discuss with your physician which treatment may be best for you.






Leave A Comment