Knee pain that develops acutely after an injury sustained in a car accident or on the job can be a result of numerous factors. Some of these factors are much more serious than others and may result in a need for surgery.
Right after the injury takes place, acute pain and swelling in the knee may make it difficult for an individual to walk. A visit to an emergency room or an urgent care may be necessary. At that time, x-rays should be obtained along with application of ice and most likely a knee immobilizer for pain control. Maybe crutches as well.
difficult for an individual to walk. A visit to an emergency room or an urgent care may be necessary. At that time, x-rays should be obtained along with application of ice and most likely a knee immobilizer for pain control. Maybe crutches as well.
With an injury that is acute, it may not even be possible for the AZ pain doctor to perform a complete physical examination. If there is no fracture and significant swelling is occurring, the typical early diagnosis is termed “internal knee derangement”.
After a few days, range of motion will probably start to improve somewhat and the swelling may go down a bit. At that point, a Phoenix pain management doctor will most likely be able to perform a better exam to see what exactly the problem is.
Ligament damage is fairly common after a significant twisting injury to the knee. This may include a rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament, which is very important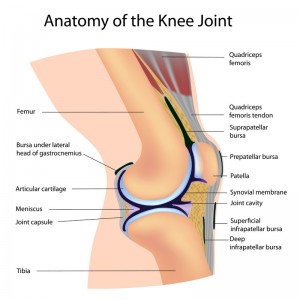 in knee stability. The pain doctor will perform stability testing for both the anterior cruciate ligament along with the posterior cruciate ligament. Instability may be indicative of a partial or a complete tear. A subsequent MRI will most likely be necessary.
in knee stability. The pain doctor will perform stability testing for both the anterior cruciate ligament along with the posterior cruciate ligament. Instability may be indicative of a partial or a complete tear. A subsequent MRI will most likely be necessary.
In addition to the front and back stabilizers, the medial and lateral collateral ligaments will be tested for stability as well. Most often, injury to these structures does not involve a complete tear and is usually allowed to heal non-surgically. Physical therapy along with pain medication may be necessary along with other treatments such as a tens unit, acupuncture, electrical stimulation and ultrasound.
One very common cause of pain after a car accident or a workplace injury is a bone bruise. This involves direct injury to the bones of the knee and also may include cartilage damage. An MRI can show a high signal in the area of damage and most often will resolve over a few weeks. If the injury led to a cartilage defect, this may cause chronic pain and swelling which may need further treatment including physical therapy, injection treatments and possibly surgical intervention.
One of the most common injuries sustained with me trauma is a meniscal tear. The meniscus is a shock absorber of the knee which is predominantly made of collagen and water along with proteoglycans. With direct trauma or a twisting injury to the knee, the meniscus can be torn which may lead to popping, locking, clicking and pain in the knee. The meniscus has a blood supply to only part of it, so often times it does not heal very well.
A minimum of 4 to 6 weeks should be attempted with conservative treatment which may include injections, physical therapy, pain medication and possibly electrical stimulation and ultrasound along with bracing.
With appropriate work up and nonoperative treatment, patients may be able to 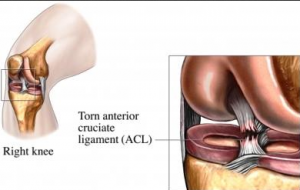 avoid surgery and get back to work. At times though, the damage to ligaments or the meniscus well necessitate surgery. There’s also the potential for tendon damage such as the patellar tendon or residual tendinitis which hopefully will resolve without the need for surgery.
avoid surgery and get back to work. At times though, the damage to ligaments or the meniscus well necessitate surgery. There’s also the potential for tendon damage such as the patellar tendon or residual tendinitis which hopefully will resolve without the need for surgery.






Leave A Comment